In today’s world of savvy shopping, earning cashback has become a desirable perk for many consumers. One of the platforms that stands out in this realm is Nectar, an innovative rewards program that lets you earn cashback on everyday purchases. If you’re tired of using discount codes or coupon codes that only save you a few pennies, Nectar offers a refreshing alternative by allowing you to accumulate real cash back on your spending, paving the way for a more rewarding shopping experience.
Nectar is a unique program designed to enhance your shopping experience by rewarding you for the purchases you already make. It partners with a variety of retailers, meaning you can earn cashback simply by shopping at your favorite stores. Whether you’re stocking up on groceries, updating your wardrobe, or even booking travel, Nectar makes it easy to earn cashback on a wide range of purchases. Unlike traditional discounts or coupon codes that often come with limitations, Nectar provides straightforward rewards that directly translate to cash in your pocket, making it a flexible and user-friendly option for any shopper.
To start earning cashback with Nectar, one effective method is to utilize the TopCashback platform. Simply create an account on TopCashback and search for Nectar’s offers among the many retailers available. Once you find what you’re looking for, click through the TopCashback link to shop as you normally would. Your transactions will be tracked, and within a few days, you’ll see your cashback balance start to grow. This process allows you to accumulate real cash back on your purchases without needing to fuss over coupon codes or seasonal discounts. It’s a seamless way to compound savings, giving you even more reasons to celebrate your shopping habits!
Q&A
**Q: What is Nectar?**
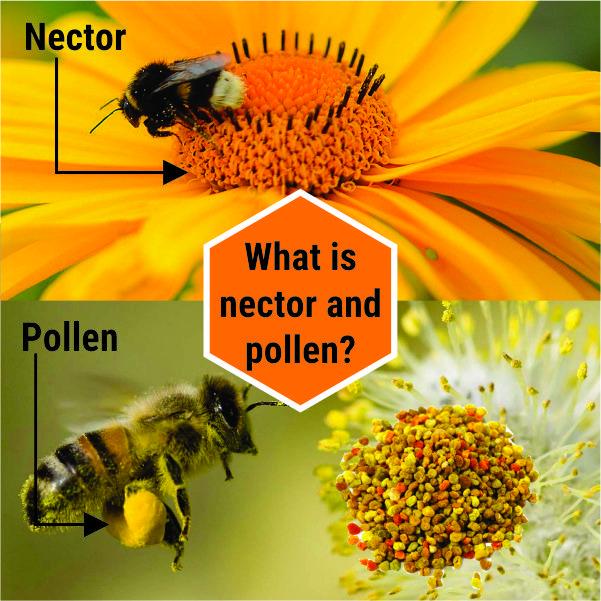
A: Nectar is a sugary fluid produced by flowering plants, primarily by glands called nectaries. It plays a pivotal role in the plant’s reproductive process by attracting pollinators like bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds with its sweetness.
—
**Q: How do plants produce nectar?**
A: Nectar production occurs in specialized glands, and the formulation can vary significantly among different species. These plants generate nectar through photosynthesis, turning sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy, which is then transformed into sugars and secreted.
—
**Q: What role does nectar play in the ecosystem?**
A: Nectar acts as a vital link in the food web, providing sustenance for a variety of creatures. Pollinators are drawn to nectar as a food source, facilitating the transfer of pollen between flowers, which is essential for fruit and seed production.
—
**Q: How do pollinators benefit from nectar?**
A: For pollinators, nectar serves as an energy source rich in carbohydrates, while also offering amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. This nutritional boost is crucial for their survival, growth, and reproductive success.
—
**Q: Are all types of nectar the same?**
A: Not at all! Nectar varies widely in composition, flavor, and scent, depending on the plant species. Some nectar may have higher sugar concentrations, while others may contain essential oils or even toxins that can deter certain herbivores.
—
**Q: Can humans use nectar?**
A: Yes! Many cultures have harnessed nectar for culinary purposes. Honey, for example, is produced by bees from nectar and is enjoyed for its sweetness and medicinal qualities. Additionally, some plants’ nectars can be brewed into beverages or used in desserts.
—
**Q: How does climate change affect nectar production?**
A: Climate change poses multiple threats to nectar-producing plants. Alterations in temperature, precipitation patterns, and seasonal shifts can disrupt blooming periods, affecting the quantity and quality of nectar available, which in turn impacts pollinator populations.
—
**Q: What can individuals do to support nectar sources and pollinators?**
A: Individuals can create pollinator-friendly gardens by planting native flowering plants that produce nectar throughout the seasons. Avoiding pesticides, providing water sources, and creating habitats will also help support local pollinator populations.
—
**Q: Can nectar influence the behavior of pollinators?**
A: Definitely! Nectar’s sugar concentration, scent, and availability can influence pollinator visitation patterns. Some species prefer certain plants based on nectar quality, which can lead to varied interactions within the ecosystem.
—
**Q: What’s the relationship between nectar and fruit production?**
A: Nectar is essential for pollination, which leads to fruit development. When pollinators transfer pollen from flower to flower, it fertilizes the ovules, enabling the plant to produce fruits containing seeds for the next generation. This interconnected relationship is vital for biodiversity and food supply.
—
**Q: Are there any myths about nectar?**
A: There are several myths surrounding nectar, one being that all nectar is safe to consume. While many nectar sources are edible, some can be toxic. It’s essential to be knowledgeable about which plants produce safe nectar for consumption.
—
This Q&A dives into the fascinating world of nectar, unraveling its essential role in nature and its connection with pollinators, ecosystems, and even human cultures.